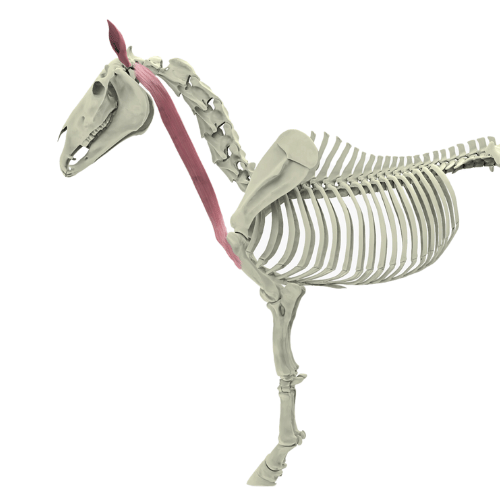
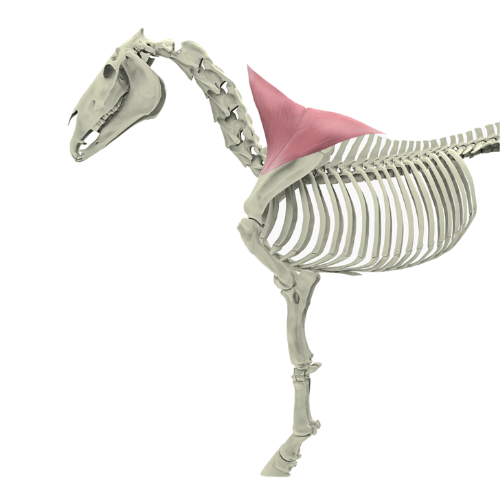
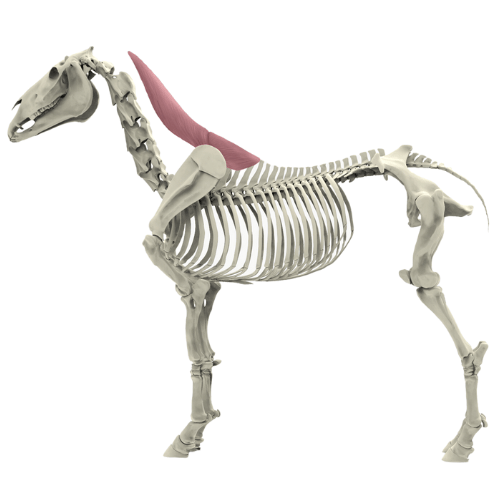
The musculus trapezius, better known as the trapezius muscle, is a central muscle for the mobility of the shoulder girdle and plays an important role in the stabilization and movement of the forelimb. It belongs to the group of limb carriers, as it is closely connected with the mobility of the shoulder and the suspension of the forelimb. Despite its essential function, the trapezius muscle is often overlooked when it comes to the health and mobility of the horse.
Anatomy of the Trapezius Muscleat the horse
The trapezius muscle extends over a large area of the horse's body and is divided into two main parts:
Pars cervicalis (anterior part): This part of the trapezius muscle extends from the 2nd cervical vertebra to the shoulder blade and is particularly responsible for the movements of the neck region as well as the protraction of the forelimbs.
Pars thoracica (posterior part): This part extends from the 2nd to the 10th thoracic vertebra to the scapula and ensures that the scapula is moved backward, which is important for supporting the shoulder during movement and the abduction of the forelimbs.

The trapezius muscle in the horse is responsible for various movements, particularly:
-
The flexion and abduction of the forelegs, i.e., lifting and lateral spreading of the forelegs.
- The movement of the shoulder blade forward and backward, which is crucial for a smooth and fluid movement of the horse during canter and trot.
- Supports neck movement by stabilizing the shoulder blade and allowing elastic suspension of the shoulder.
The trapezius muscle and its role in shoulder stabilization
Unlike humans, horses do not have a collarbone, so the horse's shoulder is stabilized only by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. The trapezius muscle plays a crucial role here by fixing the shoulder blade from the outside, ensuring that the horse has free mobility and power transfer from the forehand to the trunk.
In an optimally trained condition and with good equipment, the trapezius muscle is not much wider in cross-section than one or two fingers. Nevertheless, its function should not be underestimated, as it is responsible for the coordination of the forelegs and the mobility of the entire upper body.
Problems in the Trapezius Muscle: Causes and Symptoms
A poorly functioning or tense trapezius muscle can lead to several movement problems in horses. One of the most common causes of issues in the trapezius muscle is ill-fitting equipment, such as an unsuitable saddle. This can result in muscle overload and tension, significantly impairing the horse's mobility.
Symptoms that may indicate problems in the trapezius muscle include, among others:
Difficulties with lateral movement: Since the trapezius muscle is also responsible for shoulder mobility, a blockage or tension can lead to difficulties with lateral movements such as shoulder-in or traversals.
Restricted mobility of the foreleg: The horse may have difficulty fully bringing forward or lifting the foreleg, which can be particularly problematic when working with obstacles or jumping.
Tension and Muscle Atrophy: When the trapezius muscle is tense for an extended period, it can lead to visible dents or muscle atrophy in the trapezius area. These changes are often an indication that the muscle is overloaded or that the horse has previously suffered from inappropriate equipment or strain.
More difficult movement coordination: A tense shoulder blade and limited mobility of the trapezius muscle can lead to a general coordination disorder in the horse, causing it to move unevenly or have difficulties while galloping.
This is how you can relieve tension and fascial adhesions in the trapezius muscle of your horse
With the NeedleyRoll fascia and massage roller for horses, the entire M. trapezius on both sides can be worked on evenly. Start with little to no pressure and proceed carefully. Pay close attention to your horse's reactions to find out what feels good for them. Stay mindful and try different pressure levels and movements to gently release tension and adhesions and relax the muscle.


Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.