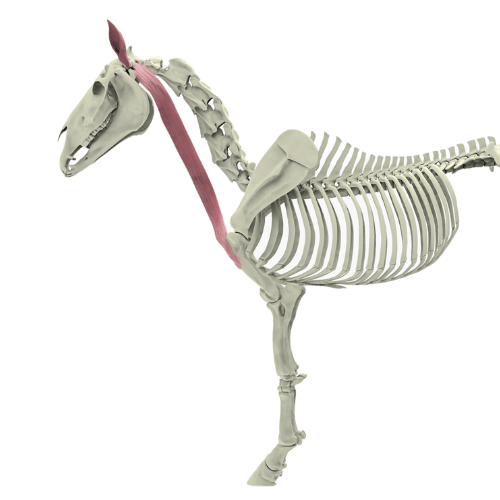
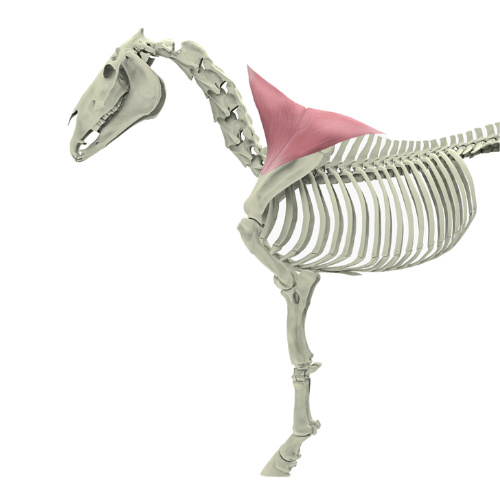
The brachiocephalicus muscle is an important muscle in the shoulder girdle musculature of the horse, responsible for a variety of movements and thus having a significant impact on the overall mobility of the animal. As part of the cranial group of shoulder muscles, it plays a central role in forward movement, head and neck flexion, as well as the movement of the forelimbs.
Anatomy of the brachiocephalic muscle
The brachiocephalicus muscle consists of two distinct parts: the cleidobrachialis muscle and the cleidocephalicus muscle. These two muscles have different origins and functions, which together constitute the function of the entire brachiocephalicus muscle.
- Musculus cleidobrachialis: This part of the muscle runs from the clavicle rudiment (a remnant of the collarbone) to the humerus (upper arm bone). It is primarily responsible for the forward movement of the forelimbs.
- Musculus cleidocephalicus: This muscle runs from the temporal bone (more precisely from the mastoid process) to the shoulder region. Its function is to lower the neck and bend the head and neck sideways, as needed.
- /wp:list-item
Together, these muscles produce a variety of movements: they not only contribute to forward movement but also help control and stabilize the horse's head and neck.
The importance of the M. brachiocephalicus for forward movement
An important aspect of the brachiocephalicus muscle is its role in the forward movement of the horse. Through the contraction of the cleidobrachialis muscle, the forelimb is pulled forward during the swing phase, which is essential for the normal movement pattern of a horse. With well-developed musculature, the horse can perform smooth and effective movement at walk, trot, and gallop.
The cleidocephalicus muscle also acts supportively, as it helps to lower the neck and stabilize the head when contracted on both sides. When contracted on one side, the head and neck are pulled to the side, which is especially important during turns and lateral movements.
/wp:paragraph
wp:heading
Tensions and problems in the area of the M. brachiocephalicus
Tensions in the area of the M. brachiocephalicus are particularly common in horses that suffer from improper training or unfavorable riding conditions. The most common causes of tension in this area include:
-
Incorrectly tied horses: If a horse is tied too tightly or incorrectly, the muscles in the neck and shoulder area, including the brachiocephalicus muscle, can become improperly tense. This leads to restricted mobility of the neck and forelimbs.
-
Riding with a hollowed back: If the horse is not moving in the correct balance and is pressing its back under the rider (e.g., due to incorrect aids), the brachiocephalicus muscle is more heavily strained and tends to become tense.
- Missing exercise: Insufficient exercise or the lack of proper training and stretching of the muscles can also lead to tension.
In affected horses, symptoms often include an underdeveloped underside of the neck and limited mobility of the neck and forelimbs.
Proper training of the horse is crucial to avoid tension in the area of the M. brachiocephalicus. A horse should learn to carry its neck and head in a natural posture without causing unnecessary muscle tension.
Equally important is to pay attention to properly fitted equipment, especially when using bridles and bits. Equipment that is too tight or improperly fitted can lead to excessive strain on the muscles and cause harmful tension and damage in the long term.
This is how you can relieve tension and fascial adhesions in the brachiocephalicus muscle of your horse
With the NeedleyRoll fascia and massage roller for horses, the entire brachiocephalicus muscle on both sides can be evenly worked on. Start with little to no pressure and proceed carefully. Pay close attention to your horse's reactions to find out what feels good for them. Stay mindful and try different pressure levels and movements to gently release tension and adhesions and relax the muscle.


Leave a comment
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.